AutoNeuroNet is a fully implemented automatic differentiation engine with custom matrices, a full neural network architecture, and a training pipeline. It comes with Python bindings via PyBind11, enabling quick, easy network development in Python, backed by C++ for enhanced speed and performance.
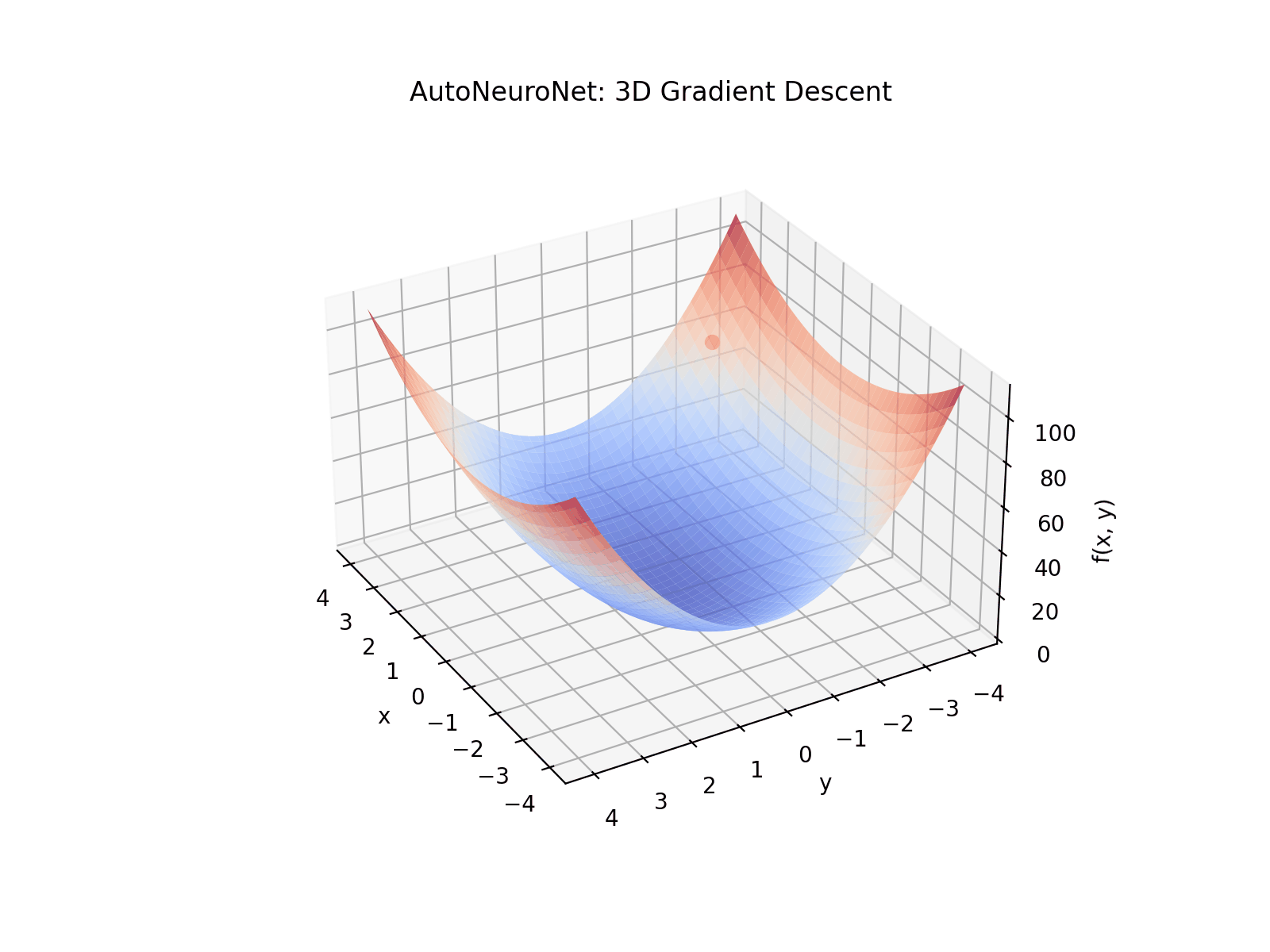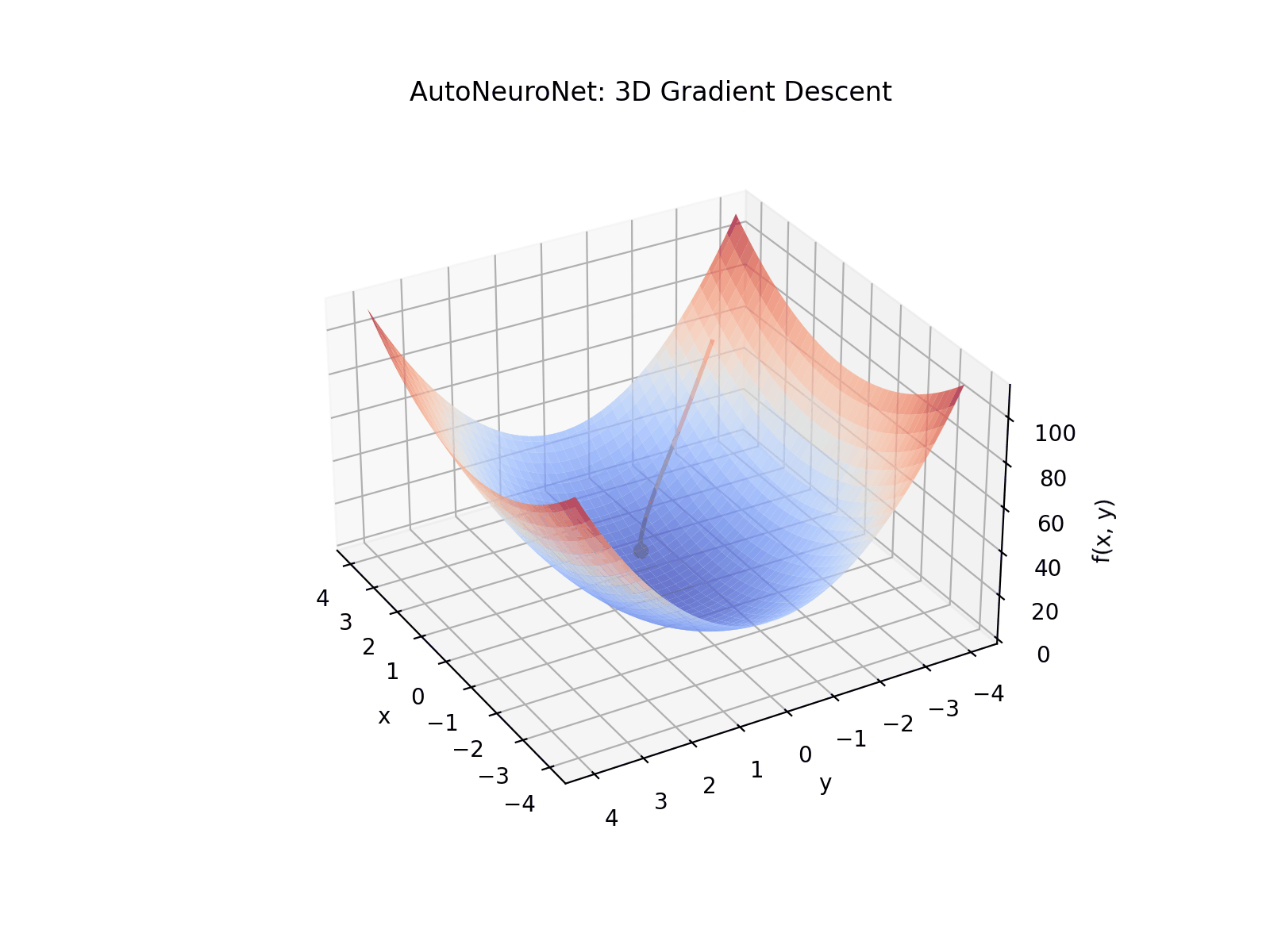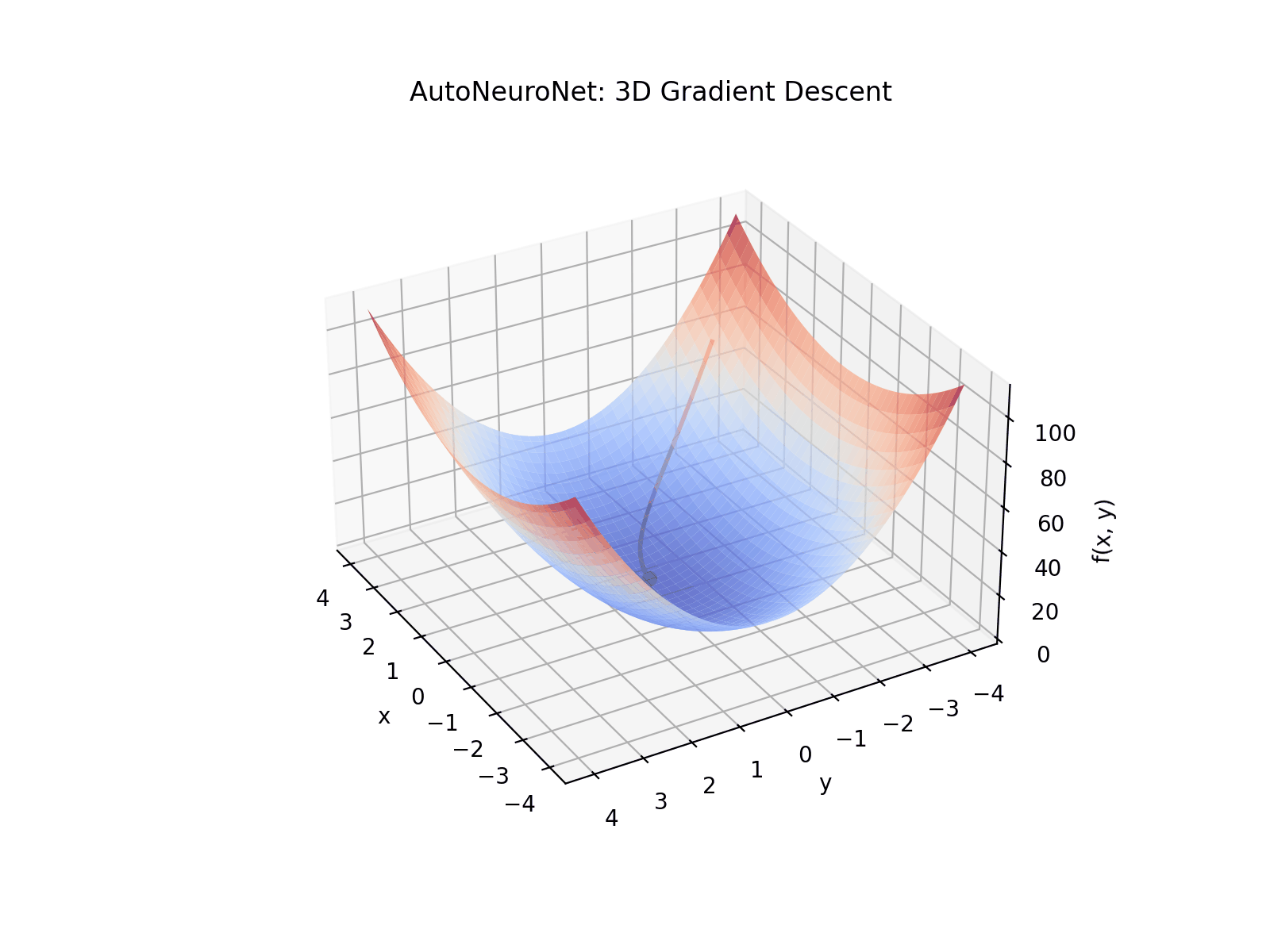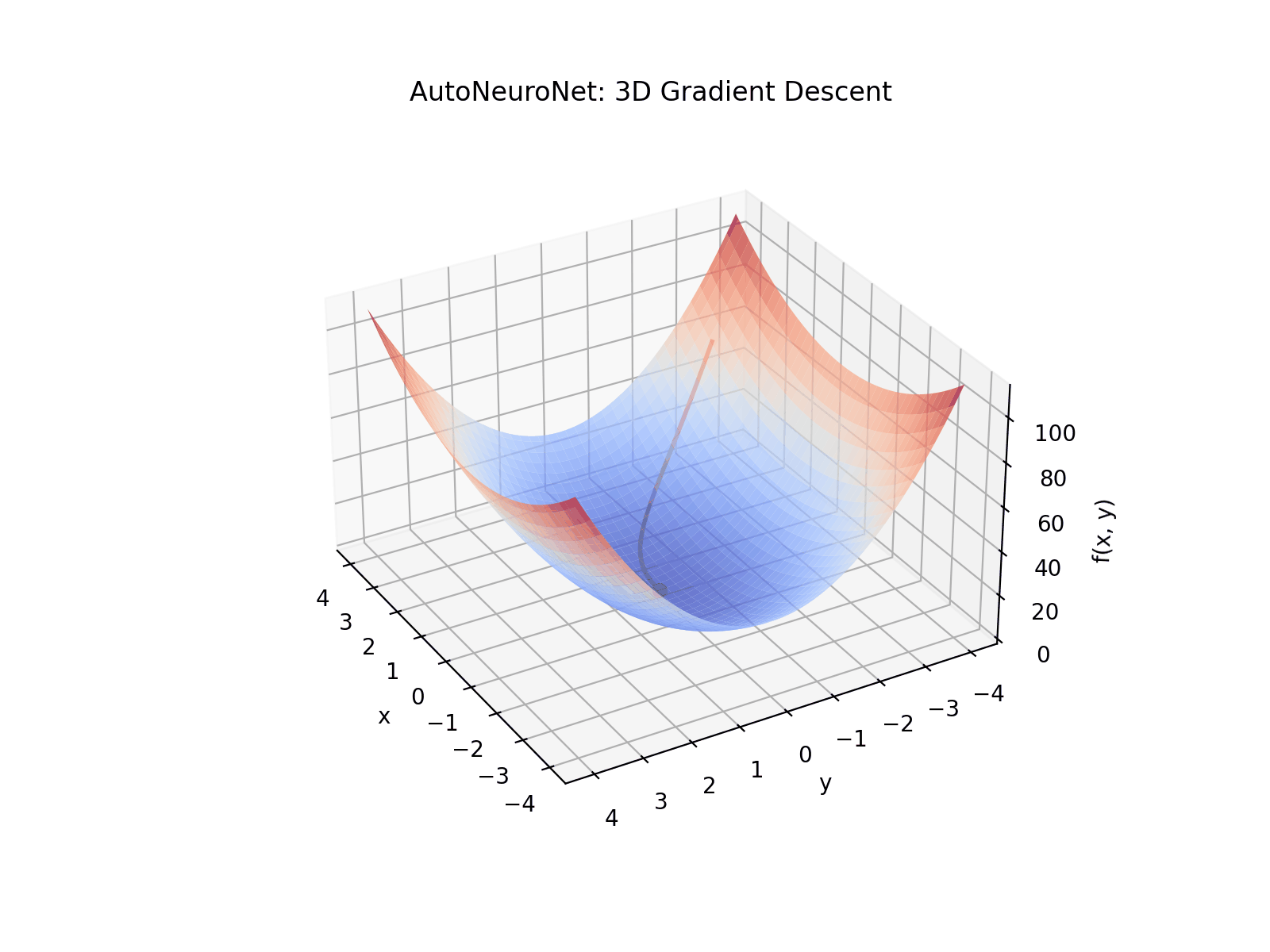
See AutoNeuroNet in action with a simple 3D visualization of gradient descent through reverse-mode automatic differentiation and backpropagation of gradients:
Install AutoNeuroNet with PIP:
pip install autoneuronetSee the full documentation at https://rishabsa.github.io/AutoNeuroNet/
To get started with AutoNeuroNet, import the package. AutoNeuroNet allows you to make automatically differentiable variables and matrices easily through the Var and Matrix classes, which store values and gradients as doubles.
Scalar Automatic Differentiation
import autoneuronet as ann
x = ann.Var(2.0)
y = x**2 + x * 3.0 + 1.0
# Set the final gradient to 1.0 and perform Backpropagation
y.setGrad(1.0)
y.backward()
print(f"y: {y.val}") # 11.0 = (2)^2 + 3x + 1
print(f"dy/dx: {x.grad}") # 7.0 = 2x + 3Matrix Initialization
import autoneuronet as ann
X = ann.Matrix(10, 1) # shape: (10, 1)
y = ann.Matrix(10, 1) # shape: (10, 1)
for i in range(n_samples):
X[i, 0] = ann.Var(i)
y[i, 0] = 5.0 * i + 3.0 # y = 5x + 3Matrix Math
import autoneuronet as ann
X = ann.Matrix(2, 2)
X[0] = [1.0, 2.0]
X[1] = [3.0, 4.0]
Y = ann.Matrix(2, 2)
Y[0] = [5.0, 6.0]
Y[1] = [7.0, 8.0]
# Z = ann.matmul(X, Y)
Z = X @ Y
print(Z)
# Output:
# Matrix(2 x 2) =
# 19.000000 22.000000
# 43.000000 50.000000NumPy to Matrix
import autoneuronet as ann
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]])
X = ann.numpy_to_matrix(x)
print(X)
# Output:
# Matrix(2 x 2) =
# 1.000000 2.000000
# 3.000000 4.000000Neural Networks, Loss Functions, and Optimizers
AutoNeuroNet supports several types of layers, including Linear fully-connected layers and activations functions such as ReLU, Sigmoid, or Softmax.
import autoneuronet as ann
import numpy as np
model = ann.NeuralNetwork(
[
ann.Linear(784, 256, init="he"),
ann.ReLU(),
ann.Linear(256, 128, init="he"),
ann.ReLU(),
ann.Linear(128, 10, init="he"),
ann.Softmax(),
]
)
optimizer = ann.SGDOptimizer(
learning_rate=1e-2, model=model, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=1e-4
)
print(model)AutoNeuroNet also supports several loss functions, such as the MSELoss, MAELoss, BCELoss, CrossEntropyLoss, and CrossEntropyLossWithLogits, and optimzers, such as GradientDescentOptimizer and SGDOptimizer.
loss = ann.MSELoss(labels, logits)
loss.setGrad(1.0)
loss.backward()
optimizer.optimize()
optimizer.resetGrad()
print(f"Loss: {loss.getVal()}")Reference Resources used in the development of AutoNeuroNet: