Stop chunking blindly. Combine the structure of Tree-Search with the reasoning of Knowledge Graphs. Runs locally or in the cloud.
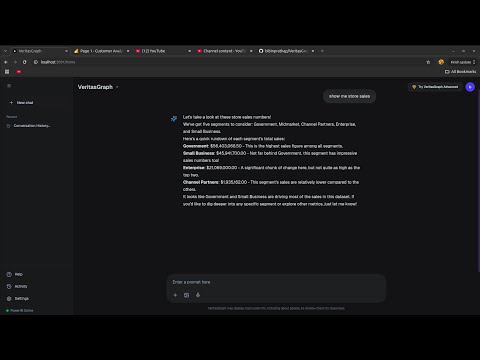
🎯 Traditional RAG guesses based on similarity. VeritasGraph reasons based on structure.
Don't just find the document—understand the connection.
|
Why choose? VeritasGraph includes the hierarchical "Table of Contents" navigation of PageIndex PLUS the semantic reasoning of a Knowledge Graph. |
|
| Feature | Vector RAG | PageIndex | VeritasGraph |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retrieval Type | Similarity | Tree Search | 🏆 Tree + Graph Reasoning |
| Attribution | ❌ Low | ✅ 100% Verifiable | |
| Multi-hop Reasoning | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Tree Navigation (TOC) | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Semantic Search | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Cross-section Linking | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Visual Graph Explorer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Built-in UI |
| Power BI Integration | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Native MCP |
| 100% Local/Private | ❌ Cloud | ✅ On-Premise | |
| Open Source | ❌ Proprietary | ✅ MIT License | |
| Cross-section linking | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
VeritasGraph is a production-ready framework that solves the fundamental problem with vector-search RAG: context blindness. While traditional RAG chunks your documents into isolated fragments and hopes cosine similarity finds the right one, VeritasGraph builds a knowledge graph that actually understands how your information connects.
The result? Multi-hop reasoning that answers complex questions, transparent attribution for every claim, and a hierarchical tree structure that navigates documents like a human would—all running on your own infrastructure.
No GPU? No problem. Try VeritasGraph instantly:
pip install veritasgraph
veritasgraph demo --mode=liteThat's it. This launches an interactive demo using cloud APIs (OpenAI/Anthropic)—no local models required.
💡 What you're seeing: A query triggers multi-hop reasoning across the knowledge graph. Nodes light up as connections are discovered, showing exactly how the answer was found—not just what was found.
| Mode | Best For | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
--mode=lite |
Quick demo, no GPU | OpenAI/Anthropic API key |
--mode=local |
Privacy, offline use | Ollama + 8GB RAM |
--mode=full |
Production, all features | Docker + Neo4j |
# Lite mode (cloud APIs, zero setup)
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..."
veritasgraph demo --mode=lite
# Local mode (100% offline with Ollama)
veritasgraph demo --mode=local --model=llama3.2
# Full mode (complete GraphRAG pipeline)
veritasgraph start --mode=full# Basic install (includes lite mode)
pip install veritasgraph
# With optional dependencies
pip install veritasgraph[web] # Gradio UI + visualization
pip install veritasgraph[graphrag] # Microsoft GraphRAG integration
pip install veritasgraph[ingest] # YouTube & web article ingestion
pip install veritasgraph[all] # EverythingOnce you're ready to integrate VeritasGraph into your code:
from veritasgraph import VisionRAGPipeline
# Simplest usage - auto-detects available models
pipeline = VisionRAGPipeline()
doc = pipeline.ingest_pdf("document.pdf")
result = pipeline.query("What are the key findings?")
print(result.answer)🔧 Advanced: Custom Configuration
from veritasgraph import VisionRAGPipeline, VisionRAGConfig
# Configure for local Ollama models
config = VisionRAGConfig(vision_model="llama3.2-vision:11b")
pipeline = VisionRAGPipeline(config)
# Ingest a PDF document (automatically extracts hierarchical structure)
doc = pipeline.ingest_pdf("document.pdf")
# Query with full visual context
result = pipeline.query("What are the key findings in the tables?")The Power of PageIndex's Tree + The Flexibility of a Graph
VeritasGraph now combines two powerful retrieval paradigms:
- Tree-based navigation - Human-like retrieval through Table of Contents structure
- Graph-based search - Semantic similarity across the entire document
from veritasgraph import VisionRAGPipeline
pipeline = VisionRAGPipeline()
doc = pipeline.ingest_pdf("report.pdf")
# View the document's hierarchical structure (like a Table of Contents)
print(pipeline.get_document_tree())
# Output:
# Document Root
# ├── [1] Introduction (pp. 1-5)
# │ ├── [1.1] Background (pp. 1-2)
# │ └── [1.2] Objectives (pp. 3-5)
# ├── [2] Methodology (pp. 6-15)
# │ ├── [2.1] Data Collection (pp. 6-10)
# │ └── [2.2] Analysis Framework (pp. 11-15)
# └── [3] Results (pp. 16-30)
# Navigate to a specific section (tree-based retrieval)
section = pipeline.navigate_to_section("Methodology")
print(section['breadcrumb']) # ['Document Root', 'Methodology']
print(section['children']) # [Data Collection, Analysis Framework]
# Or use graph-based semantic search
result = pipeline.query("What methodology was used?")
# Returns answer with section context: "📍 Location: Document > Methodology > Analysis Framework"| Traditional RAG | VeritasGraph with Trees |
|---|---|
| Chunks documents randomly | Preserves document structure |
| Loses section context | Maintains parent-child relationships |
| Can't navigate by structure | Supports TOC-style navigation |
| No hierarchy awareness | Full tree traversal (ancestors, siblings, children) |
veritasgraph --version # Show version
veritasgraph info # Check dependencies
veritasgraph init my_project # Initialize new project
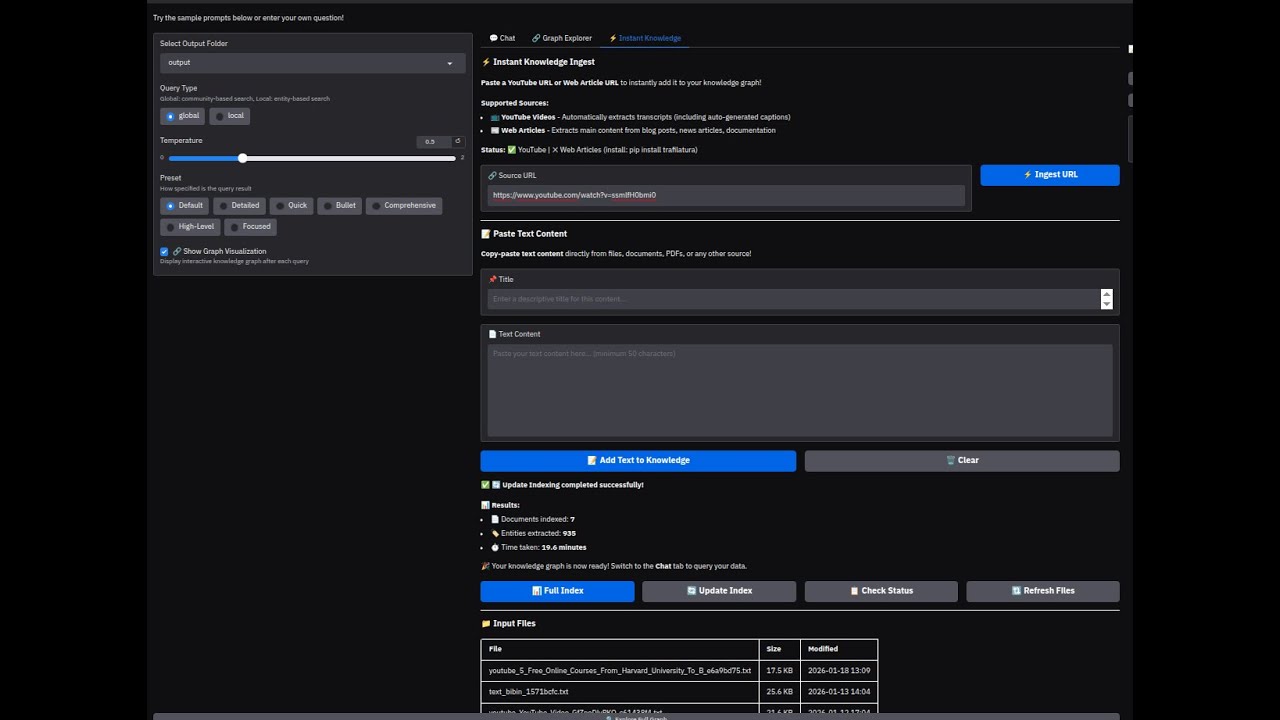
veritasgraph ingest document.pdf --ingest-mode=document-centric # Don't Chunk. Graph.VeritasGraph offers multiple ways to ingest content into your knowledge graph:
Traditional RAG splits documents into arbitrary 500-token chunks, destroying context. VeritasGraph's document-centric mode treats whole pages or sections as single retrievable nodes:
from veritasgraph import VisionRAGPipeline, VisionRAGConfig
config = VisionRAGConfig(ingest_mode="document-centric") # Tables stay intact!
pipeline = VisionRAGPipeline(config)
doc = pipeline.ingest_pdf("annual_report.pdf")Add content to your knowledge graph with one click:
| Source | How It Works |
|---|---|
| 📺 YouTube | Paste URL → auto-extracts transcript |
| 📰 Web Articles | Paste URL → extracts main content |
| 📄 PDFs | Upload → document-centric extraction |
| 📝 Text | Paste directly → instant indexing |
# CLI ingestion
veritasgraph ingest https://youtube.com/watch?v=xxx
veritasgraph ingest https://example.com/article
veritasgraph ingest document.pdf --mode=document-centric| Mode | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
document-centric |
Whole pages/sections as nodes (default) | Most documents |
page |
Each page = one node | Slide decks, reports |
section |
Each section = one node | Structured documents |
chunk |
Traditional 500-token chunks | Legacy compatibility |
🎮 Try Live Demo - Stable URL - always redirects to current server
Maintain 100% control over your data and AI models, ensuring maximum security and privacy.
Every generated claim is traced back to its source document, guaranteeing transparency and accountability.
Answer complex, multi-hop questions that go beyond the capabilities of traditional vector search engines.
Combines PageIndex-style TOC navigation with graph flexibility. Navigate documents like humans do (through sections and subsections) while also leveraging semantic search across the entire graph.
Explore your knowledge graph with an interactive 2D graph explorer powered by PyVis, showing entities, relationships, and reasoning paths in real-time.
Build a sovereign knowledge asset, free from vendor lock-in, with full ownership and customization.
Connect AI assistants to Power BI and enterprise tools through the cutting-edge Model Context Protocol standard.
VeritasGraph now includes an enterprise-grade Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for Power BI! Enable AI assistants like Claude, ChatGPT, or any MCP-compatible client to interact with your Power BI data through natural language.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that enables AI models to securely interact with external tools and data sources. Think of it as a universal API for AI assistants - allowing them to query databases, call APIs, and perform actions while maintaining security and auditability.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔄 Dual Connectivity | Connect to both Power BI Desktop (local) and Power BI Service (cloud) |
| 💬 Natural Language DAX | Execute DAX queries through conversational AI |
| 📊 34+ Tools | Comprehensive toolkit for data exploration and model management |
| 🔒 Enterprise Security | PII detection, audit logging, and configurable access policies |
| 🛡️ RLS Testing | Test Row-Level Security roles during development |
| ✏️ Safe Refactoring | PBIP-based editing preserves report visual integrity |
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AI Assistant (Claude/ChatGPT) │
└────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────┘
│ MCP Protocol
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Power BI MCP Server (34 Tools) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Security Layer │ Audit Logger │ Access Policies │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Desktop Connector │ XMLA Connector │ PBIP Connector │
└────────┬───────────────────┬────────────────┬───────────┘
▼ ▼ ▼
Power BI Desktop Power BI Service PBIP Files
Desktop Operations:
desktop_discover_instances- Auto-discover running Power BI Desktopdesktop_execute_dax- Run DAX queries with security processingdesktop_list_tables/columns/measures- Explore your data model
Cloud Operations:
list_workspaces- Access Power BI Service workspaceslist_datasets- Browse cloud-hosted datasetsexecute_dax- Query cloud data with full security
PBIP Operations (Safe Refactoring):
pbip_rename_table/column/measure- Rename without breaking visualsscan_table_dependencies- Preview rename impact before changes
# Navigate to the MCP server
cd mcp/powerbi-mcp
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Start the backend API
cd backend
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
uvicorn app:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8002
# Or run the MCP server directly
python src/server.pyFull walk-through of the Power BI MCP server: starting the backend, calling tools via the Model Context Protocol, and chatting with datasets through VeritasGraph.
User: "Show me total sales by region for Q4 2025"
AI Assistant (via MCP):
EVALUATE
SUMMARIZE(
FILTER(Sales, Sales[Date] >= DATE(2025,10,1)),
Geography[Region],
"Total Sales", SUM(Sales[Amount])
)
- Power BI MCP Server README - Full setup guide and tool reference
- Backend API Documentation - REST API endpoints
- MCP Client Setup - Next.js chat interface
A brief video demonstrating the core functionality of VeritasGraph, from data ingestion to multi-hop querying with full source attribution.
🎬 Watch on YouTube: VeritasGraph - Enterprise Graph RAG Demo
The following diagram illustrates the end-to-end pipeline of the VeritasGraph system:
graph TD
subgraph "Indexing Pipeline (One-Time Process)"
A --> B{Document Chunking};
B --> C{"LLM-Powered Extraction<br/>(Entities & Relationships)"};
C --> D[Vector Index];
C --> E[Knowledge Graph];
end
subgraph "Query Pipeline (Real-Time)"
F[User Query] --> G{Hybrid Retrieval Engine};
G -- "1. Vector Search for Entry Points" --> D;
G -- "2. Multi-Hop Graph Traversal" --> E;
G --> H{Pruning & Re-ranking};
H -- "Rich Reasoning Context" --> I{LoRA-Tuned LLM Core};
I -- "Generated Answer + Provenance" --> J{Attribution & Provenance Layer};
J --> K[Attributed Answer];
end
style A fill:#f2f2f2,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style F fill:#e6f7ff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style K fill:#e6ffe6,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
Clone the repo and run a full VeritasGraph stack (Ollama + Neo4j + Gradio app) with one command:
- Update
docker/five-minute-magic-onboarding/.envwith your Neo4j password (defaults for the rest). - From the same folder run:
cd docker/five-minute-magic-onboarding docker compose up --build - Services exposed:
- Gradio UI: http://127.0.0.1:7860/
- Neo4j Browser: http://localhost:7474/
- Ollama API: http://localhost:11434/
See docker/five-minute-magic-onboarding/README.md for deeper details.
Share VeritasGraph with your team using these free deployment options:
Run with the --share flag to get a public URL instantly:
cd graphrag-ollama-config
python app.py --shareThis creates a temporary public URL like https://xxxxx.gradio.live that works for 72 hours. Perfect for quick demos!
Keep Ollama running locally while exposing the UI to the internet:
-
Install ngrok: https://ngrok.com/download (free account required)
-
Start your app locally:
cd graphrag-ollama-config python app.py --host 0.0.0.0 --port 7860 -
In another terminal, create the tunnel:
ngrok http 7860
-
Share the ngrok URL (e.g.,
https://abc123.ngrok.io) with developers.
# Install cloudflared
# Windows: winget install cloudflare.cloudflared
# Mac: brew install cloudflared
# Linux: https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-apps/install-and-setup/
# Start the tunnel
cloudflared tunnel --url http://localhost:7860For a permanent demo (without local Ollama), deploy to Hugging Face Spaces:
- Create a new Space at https://huggingface.co/spaces
- Choose "Gradio" as the SDK
- Upload your
graphrag-ollama-configfolder - Set environment variables in Space settings (use OpenAI/Groq API instead of Ollama)
| Method | Duration | Local Ollama | Setup Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
--share |
72 hours | ✅ Yes | 1 min | Quick demos |
| Ngrok | Unlimited* | ✅ Yes | 5 min | Team evaluation |
| Cloudflare | Unlimited* | ✅ Yes | 5 min | Team evaluation |
| HF Spaces | Permanent | ❌ No (use cloud LLM) | 15 min | Public showcase |
*Free tier has some limitations
VeritasGraph supports any OpenAI-compatible API, making it easy to use with various LLM providers:
| Provider | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | Cloud | Native API support |
| Azure OpenAI | Cloud | Full Azure integration |
| Groq | Cloud | Ultra-fast inference |
| Together AI | Cloud | Open-source models |
| OpenRouter | Cloud | Multi-provider routing |
| Anyscale | Cloud | Scalable endpoints |
| LM Studio | Local | Easy local deployment |
| LocalAI | Local | Docker-friendly |
| vLLM | Local/Server | High-performance serving |
| Ollama | Local | Default setup |
-
Copy the configuration files:
cd graphrag-ollama-config cp settings_openai.yaml settings.yaml cp .env.openai.example .env -
Edit
.envwith your provider settings:# Example: OpenAI GRAPHRAG_API_KEY=sk-your-openai-api-key GRAPHRAG_LLM_MODEL=gpt-4-turbo-preview GRAPHRAG_LLM_API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1 GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_MODEL=text-embedding-3-small GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1
-
Run GraphRAG:
python -m graphrag.index --root . --config settings_openai.yaml python app.py
Mix different providers for LLM and embeddings (e.g., Groq for fast LLM + local Ollama for embeddings):
GRAPHRAG_API_KEY=gsk_your-groq-key
GRAPHRAG_LLM_MODEL=llama-3.1-70b-versatile
GRAPHRAG_LLM_API_BASE=https://api.groq.com/openai/v1
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_KEY=ollama
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_MODEL=nomic-embed-text
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_BASE=http://localhost:11434/v1📖 Full documentation: See OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_API.md for detailed provider configurations, environment variables reference, and troubleshooting.
You can easily switch between different LLM providers by editing your .env file. Here are the most common configurations:
# LLM - Ollama
GRAPHRAG_API_KEY=ollama
GRAPHRAG_LLM_MODEL=llama3.1-12k
GRAPHRAG_LLM_API_BASE=http://localhost:11434/v1
# Embeddings - Ollama
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_MODEL=nomic-embed-text
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_BASE=http://localhost:11434/v1
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_KEY=ollama# LLM - OpenAI
GRAPHRAG_API_KEY=sk-proj-your-key
GRAPHRAG_LLM_MODEL=gpt-4-turbo-preview
GRAPHRAG_LLM_API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1
# Embeddings - OpenAI
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_MODEL=text-embedding-3-small
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_KEY=sk-proj-your-keyBest of both worlds - powerful cloud LLM with local embeddings for privacy:
# LLM - OpenAI
GRAPHRAG_API_KEY=sk-proj-your-key
GRAPHRAG_LLM_MODEL=gpt-4-turbo-preview
GRAPHRAG_LLM_API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1
# Embeddings - Ollama (local)
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_MODEL=nomic-embed-text
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_BASE=http://localhost:11434/v1
GRAPHRAG_EMBEDDING_API_KEY=ollama| Provider | API Base | API Key | Example Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ollama | http://localhost:11434/v1 |
ollama |
llama3.1-12k |
| OpenAI | https://api.openai.com/v1 |
sk-proj-... |
gpt-4-turbo-preview |
| Groq | https://api.groq.com/openai/v1 |
gsk_... |
llama-3.1-70b-versatile |
| Together AI | https://api.together.xyz/v1 |
your-key | meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-Turbo |
| LM Studio | http://localhost:1234/v1 |
lm-studio |
(model loaded in LM Studio) |
⚠️ Important: Embeddings must match your index! If you indexed withnomic-embed-text(768 dimensions), you must query with the same model. Switching embedding models requires re-indexing your documents.
I'm using Ollama ( llama3.1) on Windows / Linux and Ollama (nomic-text-embed) for text embeddings
Please don't use WSL if you use LM studio for embeddings because it will have issues connecting to the services on Windows (LM studio)
Ollama's default context length is 2048, which might truncate the input and output when indexing
I'm using 12k context here (10*1024=12288), I tried using 10k before, but the results still gets truncated
Input / Output truncated might get you a completely out of context report in local search!!
Note that if you change the model in setttings.yaml and try to reindex, it will restart the whole indexing!
First, pull the models we need to use
ollama serve
# in another terminal
ollama pull llama3.1
ollama pull nomic-embed-text
Then build the model with the Modelfile in this repo
ollama create llama3.1-12k -f ./Modelfile
First, activate the conda enviroment
conda create -n rag python=<any version below 3.12>
conda activate rag
Clone this project then cd the directory
cd graphrag-ollama-config
Then pull the code of graphrag (I'm using a local fix for graphrag here) and install the package
cd graphrag-ollama
pip install -e ./
You can skip this step if you used this repo, but this is for initializing the graphrag folder
pip install sympy
pip install future
pip install ollama
python -m graphrag.index --init --root .
Create your .env file
cp .env.example .env
Move your input text to ./input/
Double check the parameters in .env and settings.yaml, make sure in setting.yaml,
it should be "community_reports" instead of "community_report"
Then finetune the prompts (this is important, this will generate a much better result)
You can find more about how to tune prompts here
python -m graphrag.prompt_tune --root . --domain "Christmas" --method random --limit 20 --language English --max-tokens 2048 --chunk-size 256 --no-entity-types --output ./prompts
Then you can start the indexing
python -m graphrag.index --root .
You can check the logs in ./output/<timestamp>/reports/indexing-engine.log for errors
Test a global query
python -m graphrag.query \
--root . \
--method global \
"What are the top themes in this story?"
First, make sure requirements are installed
pip install -r requirements.txt
Then run the app using
gradio app.py
To use the app, visit http://127.0.0.1:7860/
VeritasGraph includes an interactive 2D knowledge graph explorer that visualizes entities and relationships in real-time!
 Interactive knowledge graph showing entities, communities, and relationships
Interactive knowledge graph showing entities, communities, and relationships
 Query responses with full source attribution and graph visualization
Query responses with full source attribution and graph visualization
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Query-aware subgraph | Shows only entities related to your query |
| Community coloring | Nodes grouped by community membership |
| Red highlight | Query-related entities shown in red |
| Node sizing | Bigger nodes = more connections |
| Interactive | Drag, zoom, hover for entity details |
| Full graph explorer | View entire knowledge graph |
- After each query, the system extracts the relevant subgraph (nodes/edges) used for reasoning
- PyVis generates an interactive HTML visualization
- Switch to the 🔗 Graph Explorer tab to see the visualization
- Click "Explore Full Graph" to view the entire knowledge graph
Use the checkbox "🔗 Show Graph Visualization" in the left panel to enable/disable automatic graph updates after each query.
VeritasGraph includes a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that integrates the GraphRAG knowledge graph with Power BI, enabling intelligent dataset selection and DAX query generation.
┌─────────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ Next.js Client │────▶│ Power BI MCP Server │────▶│ GraphRAG API │
│ (Chat Interface) │ │ (Python + MCP) │ │ (FastAPI) │
└─────────────────────┘ └──────────────────────┘ └─────────────────────┘
│ │ │
│ ▼ ▼
│ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ │ Power BI API │ │ Knowledge Graph │
│ │ (REST/XMLA) │ │ (Parquet Files) │
└──────────────────┴──────────────────┴─────────┴─────────────────────┘
| Component | Location | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GraphRAG API | graphrag-ollama-config/api.py |
7860 | REST API exposing GraphRAG search functions |
| Power BI MCP Server | mcp/powerbi-mcp/src/server.py |
- | MCP server with Power BI tools |
| Next.js Client | mcp/Client/ |
3000 | Chat interface for interacting with Power BI |
| Endpoint | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
/health |
GET | Health check and index status |
/query |
POST | Execute GraphRAG queries (local/global search) |
/ingest |
POST | Ingest text content into knowledge graph |
/index |
POST | Trigger GraphRAG indexing |
/status |
GET | Get current indexing status |
/files |
GET | List input files |
-
Start GraphRAG API Server:
cd graphrag-ollama-config python api.py --host 127.0.0.1 --port 7860
Or use the startup script:
.\start-graphrag-api.ps1
-
Start Ollama (LLM):
ollama serve
-
Start the MCP Client:
cd mcp/Client npm run dev -
Access the Chat Interface:
- Open http://localhost:3000
- Chat with your Power BI data using natural language
The Power BI MCP server provides these tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
list_workspaces |
List all Power BI workspaces |
list_datasets |
List datasets in a workspace |
get_tables |
Get tables from a dataset |
get_columns |
Get columns from a table |
execute_dax |
Execute DAX queries |
suggest_dataset_for_query |
Use knowledge graph to suggest best dataset |
generate_dax_with_context |
Generate DAX with schema-aware context |
index_schema_to_knowledge |
Index Power BI schema to GraphRAG |
Set these environment variables in mcp/Client/.env:
PYTHON_PATH=C:/Projects/graphrag/VeritasGraph/.venv/Scripts/python.exe
MCP_SERVER_SCRIPT=c:/Projects/graphrag/VeritasGraph/mcp/powerbi-mcp/src/server.py
LLM_API_URL=http://127.0.0.1:11434/v1/chat/completions
LLM_MODEL=llama3.1:latest
GRAPHRAG_API_URL=http://127.0.0.1:7860
POWERBI_ACCESS_TOKEN=<your-power-bi-token>Query the chat interface with natural language:
"Show me the top 10 customers by revenue from last month"
The system will:
- Query the GraphRAG knowledge graph for relevant schema context
- Identify the appropriate Power BI dataset
- Generate a valid DAX query
- Execute it against Power BI
- Return formatted results with source attribution
- Core Capabilities
- The Architectural Blueprint
- Beyond Semantic Search
- Secure On-Premise Deployment Guide
- API Usage & Examples
- Project Philosophy & Future Roadmap
- Acknowledgments & Citations
VeritasGraph integrates four critical components into a cohesive, powerful, and secure system:
- Multi-Hop Graph Reasoning – Move beyond semantic similarity to traverse complex relationships within your data.
- Efficient LoRA-Tuned LLM – Fine-tuned using Low-Rank Adaptation for efficient, powerful on-premise deployment.
- End-to-End Source Attribution – Every statement is linked back to specific source documents and reasoning paths.
- Secure & Private On-Premise Architecture – Fully deployable within your infrastructure, ensuring data sovereignty.
The VeritasGraph pipeline transforms unstructured documents into a structured knowledge graph for attributable reasoning.
- Document Chunking – Segment input docs into granular
TextUnits. - Entity & Relationship Extraction – LLM extracts structured triplets
(head, relation, tail). - Graph Assembly – Nodes + edges stored in a graph database (e.g., Neo4j).
- Query Analysis & Entry-Point Identification – Vector search finds relevant entry nodes.
- Contextual Expansion via Multi-Hop Traversal – Graph traversal uncovers hidden relationships.
- Pruning & Re-Ranking – Removes noise, keeps most relevant facts for reasoning.
- Augmented Prompting – Context formatted with query, sources, and instructions.
- LLM Generation – Locally hosted, LoRA-tuned open-source model generates attributed answers.
- LoRA Fine-Tuning – Specialization for reasoning + attribution with efficiency.
- Metadata Propagation – Track source IDs, chunks, and graph nodes.
- Traceable Generation – Model explicitly cites sources.
- Structured Attribution Output – JSON object with provenance + reasoning trail.
Traditional RAG fails at complex reasoning (e.g., linking an engineer across projects and patents).
VeritasGraph succeeds by combining:
- Semantic search → finds entry points.
- Graph traversal → connects the dots.
- LLM reasoning → synthesizes final answer with citations.
Hardware
- CPU: 16+ cores
- RAM: 64GB+ (128GB recommended)
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU with 24GB+ VRAM (A100, H100, RTX 4090)
Software
- Docker & Docker Compose
- Python 3.10+
- NVIDIA Container Toolkit
- Copy
.env.example→.env - Populate with environment-specific values
VeritasGraph is founded on the principle that the most powerful AI systems should also be the most transparent, secure, and controllable.
The project's philosophy is a commitment to democratizing enterprise-grade AI, providing organizations with the tools to build their own sovereign knowledge assets.
This stands in contrast to reliance on opaque, proprietary, cloud-based APIs, empowering organizations to maintain full control over their data and reasoning processes.
Planned future enhancements include:
-
Expanded Database Support – Integration with more graph databases and vector stores.
-
Advanced Graph Analytics – Community detection and summarization for holistic dataset insights (inspired by Microsoft’s GraphRAG).
-
Agentic Framework – Multi-step reasoning tasks, breaking down complex queries into sub-queries.
-
Visualization UI – A web interface for graph exploration and attribution path inspection.
This project builds upon the foundational research and open-source contributions of the AI community.
We acknowledge the influence of the following works:
-
HopRAG – pioneering research on graph-structured RAG and multi-hop reasoning.
-
Microsoft GraphRAG – comprehensive approach to knowledge graph extraction and community-based reasoning.
-
LangChain & LlamaIndex – robust ecosystems that accelerate modular RAG system development.
-
Neo4j – foundational graph database technology enabling scalable Graph RAG implementations.
📜 ICASF 2025 Recognition
Presented at the International Conference on Applied Science and Future Technology (ICASF 2025).
📚 Cite This Work
If you use VeritasGraph in your research, please cite:
@article{VeritasGraph2025,
title={VeritasGraph: A Sovereign GraphRAG Framework for Enterprise-Grade AI with Verifiable Attribution},
author={Bibin Prathap},
journal={International Conference on Applied Science and Future Technology (ICASF)},
year={2025}
}